PrepAI’s standard mode offers educators a range of difficulty levels—easy, medium, and hard—in question generation.
Interactive Quiz Modes for Every Learning Journey
Assess your candidates using standard learning frameworks widely used across the world's best educational institutions. Help them prepare better with a variety of question types and problem-solving scenarios using PrepAI's 3 modes, each tailored to every individual's style, ensuring a comprehensive and engaging experience for all!
3 Modes for Every Learning Style
1. Standard Mode: Generate a variety of question types mandatory for all levels of learning
Easy MCQ
Q1: Which of the following is a primary greenhouse gas responsible for climate change?
A) Oxygen (O2)
B) Methane (CH4)
C) Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
D) Helium (He)
Educators can now tailor assessments to students’ needs by selecting the appropriate difficulty level. This adaptability ensures that assessments are challenging yet achievable, promoting learning and engagement.
Medium MCQ
Q2: What is the main purpose of the Paris Agreement in the context of climate change?
A) Promoting space exploration
B) Reducing global poverty
C) Limiting global temperature increase
D) Expanding international trade
With increasing difficulty levels, educators can create personalized learning experiences for students. They can identify individual strengths and areas for improvement, helping students progress at their own pace.
Hard MCQ
Q3: Which statement(s) about the greenhouse effect are correct?
Statement I: The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface.
Statement II: Human activities, such as deforestation, do not contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Statement III: Water vapor is the primary greenhouse gas responsible for global warming.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I and III
Apart from the difficulty levels in MCQs, educators can automatically generate descriptive questions, providing a comprehensive assessment of student’s understanding of a particular topic. This feature enhances learning by encouraging critical thinking and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Descriptive Question:
Q4: What is climate change, and how does it affect ecosystems and human societies?
Ans:Climate change, driven by human activities, involves long-term shifts in Earth’s climate. It causes disruptions in ecosystems, including biodiversity loss and altered weather patterns. Human societies face threats like rising sea levels and extreme weather events. Mitigation requires reducing emissions and adopting sustainable practices, while adaptation involves building resilience in vulnerable communities.
Additionally, educators can also create True/False and Fill in the Blanks questions, expanding the range of assessment options available.
2. HOTS Mode: Bloom's Taxonomy Made Easily Accessible
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. It divides learning into six hierarchical levels, starting with simple knowledge recall at the lowest level, and moving up to more complex skills like analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
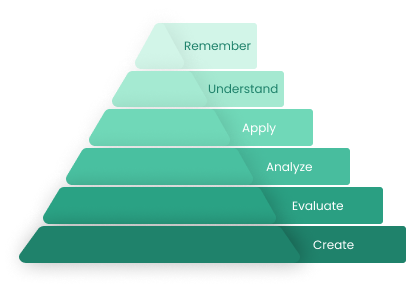
Each level of Bloom’s Taxonomy helps educators ensure students/candidates grasp basic facts and concepts, forming a strong foundation for learning and development.
Remember: Helps ensure students grasp basic facts and concepts, forming a foundation for learning.
Level 1: Remembering
Question: What is the primary greenhouse gas responsible for climate change?
A) Methane (CH4)
B) Nitrous oxide (N2O)
C) Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
D) Ozone (O3)
Understand: Allows educators to check if students can explain ideas in their own words, ensuring they understand the material.
Level 2: Understanding
Question:How does the increased concentration of greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
A) By depleting the ozone layer
B) By causing acid rain
C) By trapping heat in the Earth’s atmosphere
D) By reducing atmospheric pressure
Apply: Enables students to use what they’ve learned in new situations, showing practical knowledge.
Level 3: Application
Question:How would you propose reducing carbon emissions in a city to mitigate the impact of climate change?
Ans. Implementing strategies such as promoting renewable energy use, enhancing public transportation, and encouraging energy-efficient practices in buildings can effectively reduce carbon emissions in a city.
Question:A city plans to reduce its carbon emissions from transportation by 25% over the next decade. If the current annual emissions are 2 million metric tons, and the reduction is to be implemented linearly over the ten years, what should be the average annual reduction in metric tons?
A) 250,000 metric tons
B) 200,000 metric tons
C) 175,000 metric tons
D) 150,000 metric tons
Analyze: Helps students break down information to understand relationships, developing critical thinking skills.
Level 4: Analysis
Question:Analyze the contributing factors to the melting of polar ice caps and its implications for sea level rise.
Ans. The melting of polar ice caps is influenced by factors like rising temperatures, ocean currents, and feedback loops. It results in sea level rise, threatening coastal areas and ecosystems.
Synthesis: Promotes creativity by challenging students to combine existing parts, ideas and elements to form new ideas or products.
Level 5: Synthesis
Question:Develop a comprehensive plan for a community to adapt to the impacts of climate change, considering water scarcity, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss.
Ans. A comprehensive plan may include water conservation measures, resilient infrastructure, and community education on sustainable practices to adapt to climate change impacts.
Evaluate:Encourages students to judge the value of ideas, fostering the ability to think critically.
Level 6: Evaluation
Question: Evaluate the effectiveness of international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, in addressing and mitigating climate change.
Ans.The effectiveness of international agreements like the Paris Agreement can be assessed by considering factors such as global cooperation, emission reduction commitments, and the actual implementation of climate policies.
3. Subject Mode: Go Beyond Basics! Apply Knowledge to Solve Numericals
The subject mode in PrepAI exists to help educators easily generate numerical questions specific to the subject areas of Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, Aptitude, and many more.
Question:If sec(θ) = -5/4 and π < θ < 3π/2, find the value of sin(θ).
A) -4/5
B) -2/5
C) -3/5
D) -3/4
Question:Solve the trigonometric equation: 2cos(x) + sqrt(2) = 0 for 0 ≤ x < 2π.
A) x = 5π/4 + 2πn, for integer values of n)
B) x = π/2 + 2πn, for integer values of n)
C) x = 3π/2 + 2πn, for integer values of n)
D) x = 3π/4 + 2πn, for integer values of n)
The AI algorithm analyzes user-input formulas to create questions that reinforce concepts and test understanding. This feature helps educators save time creating quizzes, so they can focus on teaching while students can practice quickly and easily for competitive exams/trainings etc.

