Curriculum creators are responsible for designing, developing, and improving curricula. Structuring the curriculum development process through strategies will help develop a comprehensive educational program that meets the expected industry standards. Let’s discuss the role of curriculum development managers and tips to help them.
Curriculum management is the process of developing, maintaining, and improving the quality of curricula for various educational intuitions. The curriculum manager is responsible for designing and developing the curriculum with a range of content, training programs, teaching methodologies, and assessment techniques for students, learners, and employees. The developed curriculum should meet the educational standards set by the government and academic bodies.
Curriculum development and management are time-consuming tasks that involve a team of experienced people working together for a common goal. Defining the curriculum strategy, understanding the types of curriculum, and considering the various factors that affect the process is vital to developing the correct curriculum. For example, the curriculum for secondary school is different from that of high school or university.
Let’s dive into the numerous aspects of curriculum development and review the tips and strategies that can potentially save time for curriculum creators and managers.
What is Curriculum Strategy?
Curriculum strategy involves the process of defining goals, objectives, and levels to develop a curriculum that adheres to the given requirements (or finds solutions to the existing problems/ gaps in teaching). It streamlines the elements of the curriculum by defining the relationships between them. What makes a quality curriculum is the time and energy spent developing the curriculum strategy.
Elements of Curriculum Development
The elements of the curriculum are interrelated and broadly classified into the following. The success of the curriculum depends on how well the elements coordinate and align with each other.
Objectives of Curriculum
The objectives define the purpose of developing the curriculum. It answers questions such as, ‘why do we need this subject?’, ‘why is this topic included?’, ‘what is the aim of teaching this to students?’, and so on. The objectives are categorized based on behavioral, cognitive, and affective terms. The objectives depend on the learner, the learning process, society, and the knowledge shared.
Content of Curriculum
The content deals with the subjects, topics, syllabus, covered at school/ college. It is the body of knowledge the teachers impart to students. A curriculum development manager needs to be highly careful when determining the content of the curriculum. The scope of the matter to the number of courses and how the whole thing fits into the societal constraints should be analyzed. Continuity, integrity, and balance are vital to creating content that is useful, educative, and assertive.
Teaching/ Learning Methodologies
The third element of curriculum development deals with how the content is presented to students. Which teaching methodologies should teachers follow? Are the teaching processes inclusive? How can technology be used to improve the quality of teaching/ learning? What kind of assessment methods should be used to test students’ knowledge? The focus is also on the learning experience of the students, and how teachers can provide them with the necessary opportunities to practice and test their learned behavior.
Evaluation of Curriculum
Evaluating the curriculum is different from student evaluation that is covered in the teaching methodologies. This includes evaluating whether the designed curriculum satisfies the reason for which it was developed. It deals with measuring the outcome of implementing the curriculum at educational institutions.
What are the 3 Types of Curriculum?
The curriculum is classified into three major types based on the components.
- Explicit: Also known as overt or official curriculum, it details the steps to follow to properly implement the curricula to arrive at the intended outcome.
- Implicit/ Hidden: Different learning aspects contribute to implicit curricula. It is a by-product of implementing explicit curricula.
- Absent/ Excluded: Absent or null curriculum is the one that is not taught or excluded from the developed curricula. It could be intentional or unintentional.
Tips and Strategies for Curriculum Creators
- Focus on the students rather than on creating the best lesson plan. The ultimate goal should be to do what’s best for the learners.
- Talk to other experts, teachers, etc., from the industry and consider their inputs.
- Make use of technology to design the curriculum. There are different software applications to assist you.
- Avoid pre-packaged curricula. The curriculum needs to be tailor made for the intended outcome.
- Take time to design and develop the curriculum. Don’t rush through the process or skip stages.
- Make changes to the curriculum if necessary. It is acceptable and even expected if the curriculum doesn’t align with the intended outcomes.
- Create a proper evaluation and feedback system to get inputs about the curriculum. Take feedback from students and teachers.
Factors Affecting Curriculum Development
Curriculum development managers know how difficult it is to balance various factors that affect the designing and implementation of curriculum development. Ignoring any of these factors could disturb education and cause long-term complications.
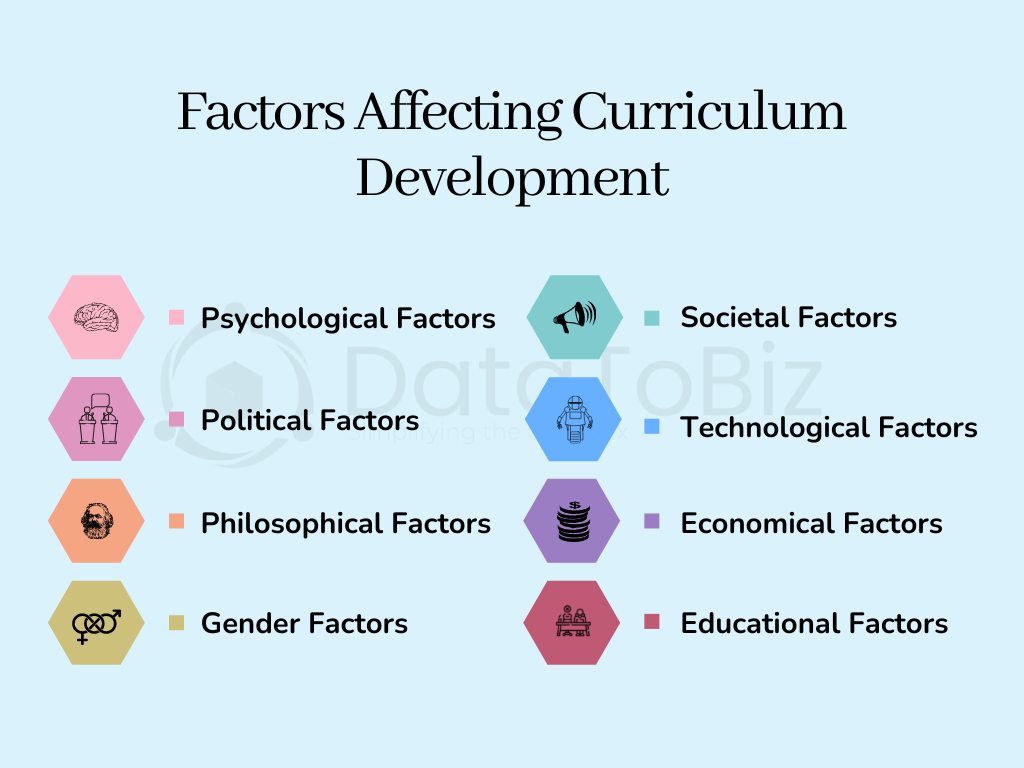
Psychological Factors
Aspects such as the nature of students, the impact of following a teaching methodology, the varying personalities of students, their perceived reactions to the subject/ teaching, etc., are considered under psychological factors.
Political Factors
Politics influence every aspect of our lives, and the curriculum is no exception. Governments have to promote nationalism and patriotism towards their countries through education. The textbook syllabus should align with the national interest while minimizing the impact of political instability.
Philosophical Factors
Philosophy is considered one of the major factors that affect curriculum development. It’s vital for the curriculum development team to believe in what they include in the plans. Being vague, unclear, or doubtful will lead to ineffective results.
Gender Factors
Gender constraints are no longer a barrier for students to limit their foray into professions. It is important to allow students to choose their professions based on their interests and preferences. The curriculum should allow every student to join a course, irrespective of their gender.
Societal Factors
How do the social elements affect the content of the curriculum? They help align the content to suit the changes in social direction by analyzing human behavior. The social background of students, teachers, schools, etc., is considered to increase flexibility, awareness, and tolerance in content and teaching methodologies.
Technological Factors
Even though all schools are not equipped to use technology for education, the curriculum should have enough flexibility to provide for technological advancement. Technology is also used for curriculum development by designing models to effectively implement the curricula for intended outcomes.
Economical Factors
Can a school run by the government or with limited funds implement the curriculum designed for an elite school? If the curriculum includes using modern technology for teaching, schools with little or no access to technology will suffer from the consequences.
Educational Factors
Providing effective education is possible only when the teachers are properly trained. The curriculum should include training programs for teachers and students. It should also focus on aspects like physical training, games, sports, drama, debates, soft skills development, and so on.
What are Essential Components of Managing Curriculum?
Curriculum creators focus on the four most important components to manage curricula development and implementation.
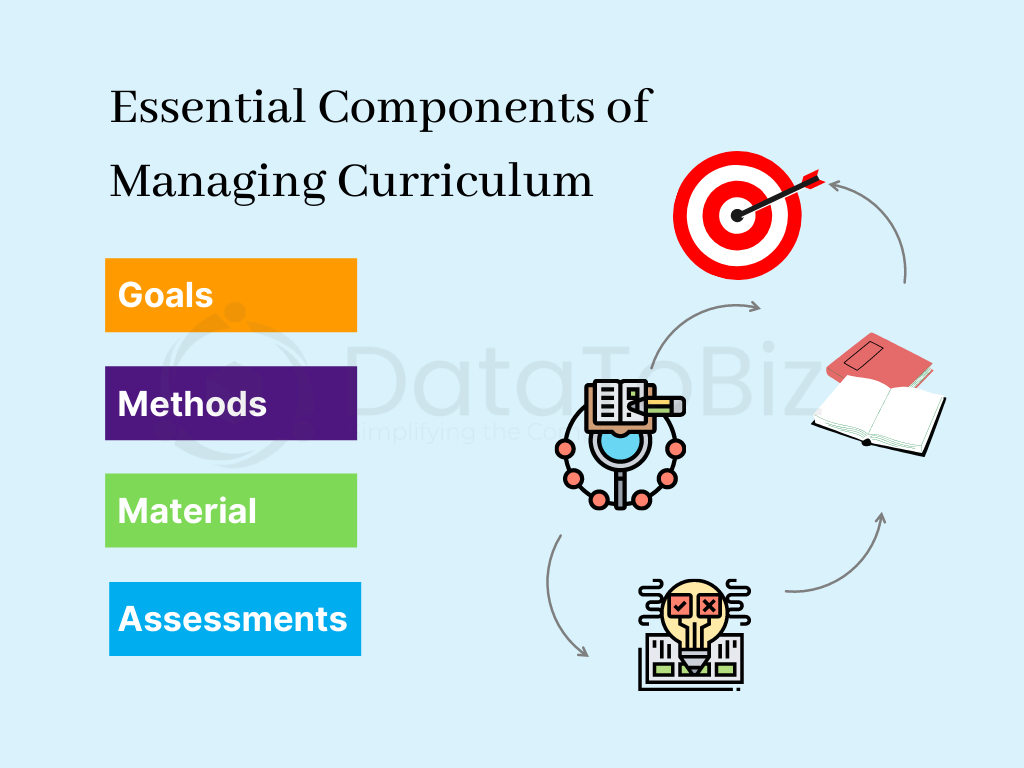
Goals: Identify measurable and actionable goals that align with the standards in the education industry and suit the requirements of the grade level. Curriculum managers need to ensure that the goals are practical and feasible enough to be achieved.
Material: What kind of teaching material will be used to implement the curriculum? While physical printed textbooks are traditional tools, audio files, digital copies, videos, graphics, etc., are now a part of the education industry.
Methods: Does the curriculum rely on traditional teaching methods? Should it be a combination of traditional and modern methodologies? Should it focus only on the modern techniques using AI tools? The curriculum managers should consider the above-mentioned factors when determining the methods of teaching.
Assessments: How should teachers assess students to determine their knowledge? What kind of assessments help get a comprehensive picture of the student’s learning abilities? How can artificial intelligence tools like PrepAI streamline assessments? Homework, projects, oral and written tests, etc., are considered as a part of assessments.
What are the 7 Stages of Curriculum Development?
Curriculum development needs to happen in a streamlined and stage-wise manner to arrive at the required outcome. Though steps can blur and merge, depending on the needs/ problems, it is vital not to skip any stage or rearrange the order. For example, you cannot list the outcomes without identifying what you even need from the curriculum, and the content cannot be finalized without understanding the needs and the outcomes.
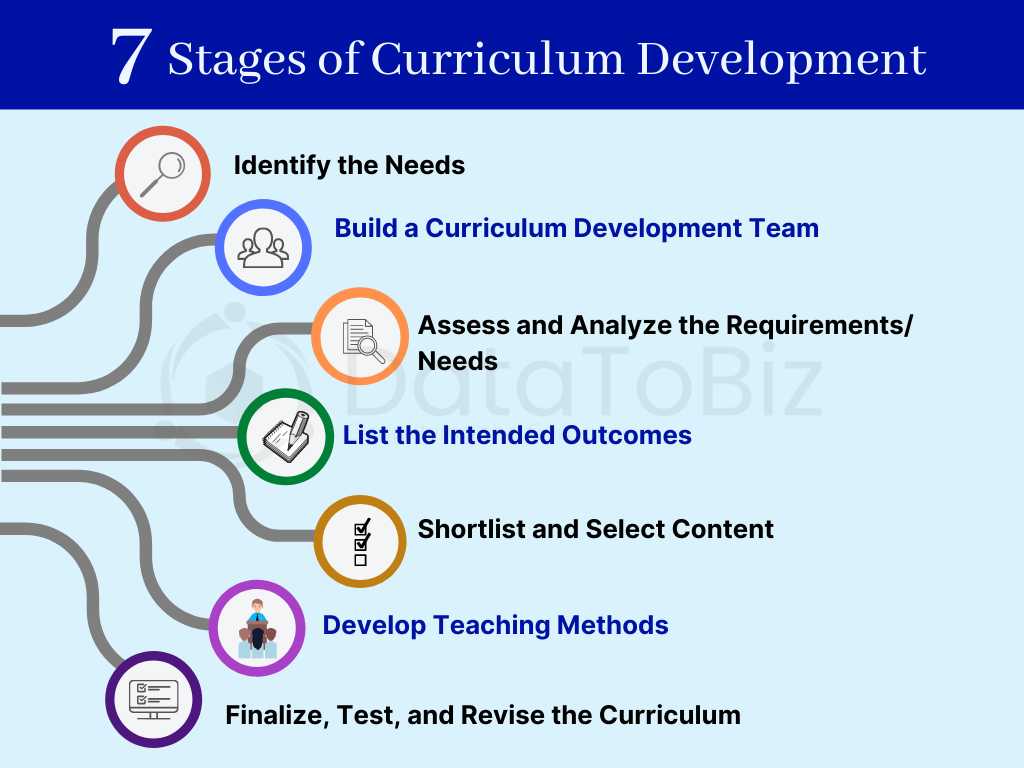
Identify the Needs
Curriculum development comes into the picture usually when there’s concern or issue raised by the target audiences. You identify the need for curriculum development by answering a list of questions of what the issue is, why it is causing a problem, and what kind of effects it has. The answers broadly define the scope of the curriculum content (mention the possible topics/ subjects that will be included).
Build a Curriculum Development Team
Designing and developing a curriculum for a target group is not one person’s job. The curriculum development manager forms a team of qualified and experienced educators/ professionals and supervises the process.
- Decide the roles and duties of the team members.
- Establish a foolproof process for selecting team members.
- Define the principles for collaboration between the curriculum development team members.
Assess and Analyze the Requirements/ Needs
This stage involves two processes-
The first is a needs assessment, where the purpose is to determine what is needed and by whom (teachers or students or both). KAP survey (Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice), focus groups, etc., are techniques covered in this process.
The second is needs analysis, which describes how the collected data and results should be used. It includes ways to identify the gaps between knowledge and practice, determine the trends, prioritize needs, and understand the characteristics of the target group.
List the Intended Outcomes
The next stage in curriculum development is to refine and reestablish the needs/ issues. This helps in making a proper list of the intended outcomes. An intended outcome is what the students/ learner will get from the curriculum.
The list should also include the components of intended outcomes such as the conditions, standards, and performance expected, some examples to clearly define and explain the intended outcomes, and an overview of learning behaviors.
Shortlist and Select Content
Finally, it’s time to select the content for the curriculum. This is a huge responsibility on the curriculum development team as the content will directly influence and impact the learner. How will the content enrich the students/ learners’ lives? What knowledge, skills, subjects, attitudes, etc., should be included in the content to provide the intended outcome to the learners?
The scope of the content and the sequence in which it should be taught are also mentioned during content selection.
Develop Teaching Methods
It’s now time to identify and design the best teaching methods to share the content effectively with the students. A learning model and its components are elaborately defined to help trainers/ teachers plan their lessons.
The teaching methods should align with the learning behaviors to create the necessary impact and successfully arrive at the intended outcome. Assessments methods are also a part of the learning model. For example, AI-based question generation solutions such as PrepAI helps teachers create assessments in minutes. Including technology in the curriculum will ease the way to adopt EdTech in mainstream educational institutions.
Finalize, Test, and Revise the Curriculum
Once the curriculum is ready, you need to evaluate it to identify loopholes or errors. Take suggestions from test sites and make the required changes to the curriculum before officially finalizing it for educational institutions.
Conclusion
Curriculum development is not about the curriculum or the plan but its value in the education industry. Curriculum creators need to consider the short-term and long-term effects of the curricula they create to encourage inclusive and healthy learning models in the industry.




